
This includes manufacturing labor and other direct labor expenses tied to production. You need to know how much you spent on goods you sold during an accounting period. This helps figure out your gross profit when subtracting COGS from your sales revenue. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) covers all the direct costs that go into making products a company sells. These costs include materials and labor directly used to create the product.
Cost of goods sold: How to calculate and record COGS
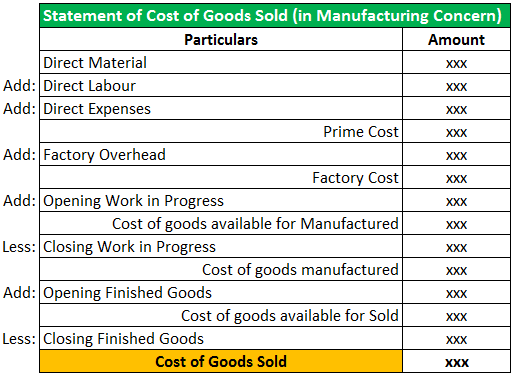
The cost of goods sold (COGS) is the cost of goods that have been sold by a business during a particular period of time. It is the cost of inventory that has been sold and is calculated by taking the beginning inventory and subtracting the ending inventory from it. COGS is an important factor in determining the gross profit of the business, and understanding the factors that impact COGS can help a business to increase its profitability. To calculate COGS, the plumber has to combine both the cost of labour and the cost of each part involved in the service.
How Often Should You Record COGS in Your Ecommerce Business?
Economic order quantity (EOQ) is the ideal order quantity a company should purchase to minimize inventory costs such as holding costs, shortage costs, and order costs. This production-scheduling model was developed in 1913 by Ford W. Harris and has been refined over time. The formula assumes that demand, ordering, and holding costs all remain constant. These are the partly processed raw materials lying on the production floor. It is unavoidable inventory which will be created in almost any manufacturing business. Gross profit is considered the first level of profitability, and it is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
Does COGS go on your income statement?
COGS includes only the direct costs of producing goods, such as raw materials and direct labor. This focus excludes indirect costs like overhead, administrative expenses, and marketing costs. While this provides clarity on the direct profitability of products, it omits significant expenses that can affect the overall profitability of the company. The basic costs of good sold journal entry for inventory purchases involves a debit and a credit. You debit the Inventory account and credit the Cash account for cash purchases or Accounts Payable for purchases on credit.
Both determine how much a company spent to produce their sold goods or services. But to calculate your profits and expenses properly, you need to understand how money flows through your business. If your business has inventory, it’s integral to understand the cost of goods sold.
- For businesses to be successful, they must be able to accurately calculate their COGS and understand the impact it has on their overall profitability.
- The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is an important component of the financial information reported by a business and is used to calculate various metrics such as gross margin and net income.
- These are the partly processed raw materials lying on the production floor.
- An important distinction to note is the difference between COGS and operating expenses (commonly referred to as OpEx).
That being said, your inventory—a component of COGS—will appear on your balance sheet as a current asset. Twitty’s Books began its 2018 fiscal year with $330,000 in sellable inventory. By the end of 2018, Twitty’s Books had $440,000 in sellable how to record cost of goods sold journal entry inventory. Under the perpetual inventory system, the inventory balance is constantly updated whenever there is an inventory in or an inventory out. Likewise, we usually record the reduction of the inventory immediately after making the sale.
Cost of goods sold is calculated at the end of an accounting period in relation to the items sold during that period. The revenue generated by a business minus its COGS is equal to its gross profit. Higher COGS with disproportionate pricing can leave your business in a deficit position if the prices are too low or alienate consumers if the price is too high.
In addition, it must maintain some supply of finished goods in order to meet demand. Under periodic inventory procedure, companies do not use the Merchandise Inventory account to record each purchase and sale of merchandise. Instead, a company corrects the balance in the Merchandise Inventory account as the result of a physical inventory count at the end of the accounting period. Also, the company usually does not maintain other records showing the exact number of units that should be on hand.
It will also overstate profitability and hide inefficiencies that you should correct. For example, COGS typically include materials, direct labor, and shipping costs. Operational expenses, however, include rent, utilities, and salaries of administrative staff. You must make sure that each costs of good sold journal entry aligns with all your other financial reports. Below is an example of a basic costs of good sold journal entry for an ecommerce business.
And during the current year, we still have a total purchase of $200,000. However, the ending inventory is determined to be $65,000 instead. Under the accrual basis of accounting, it’s recorded in the same period as the revenue from the sale, matching the expense to the income it generated.
